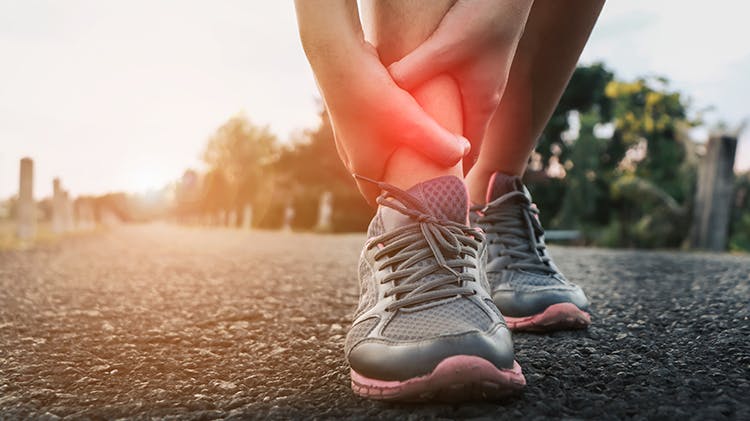
Acute Sprains and Strains: Management
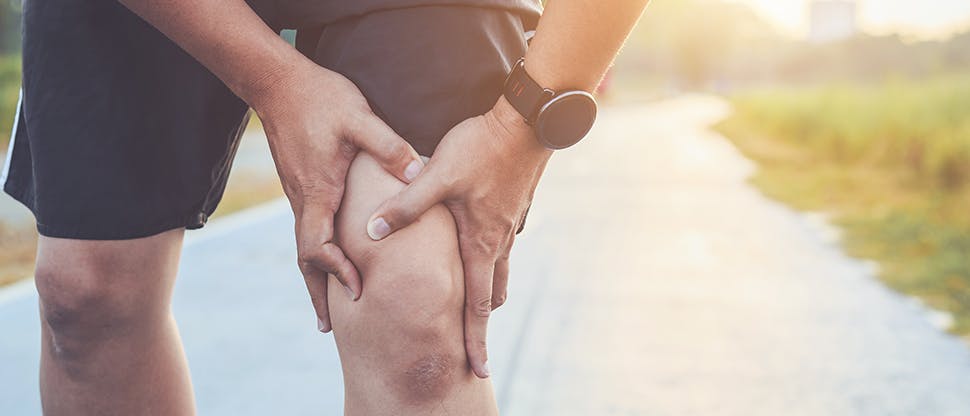

Managing muscular sprains and strains
Fortunately, sprains and strains typically respond well to treatment.
Patients with sprains and/or strains should start to feel better after 2 weeks without any intervention.1
Below we review the different approaches that could help your patient get back to enjoying their life in the case of acute, mild-moderate sprain/strain injuries.
American College of Physicians (ACP) and American Academy of Family Physicians (AAFP) clinical guideline recommendation for treating acute sprains and strains

The ACP and AAFP recommend Topical NSAIDs as 1st line and oral NSAIDs or acetaminophen as 2nd line treatments for acute, non-low back MSK pain2
The American College of Physicians (ACP) and American Academy of Family Physicians (AAFP) developed this guideline to provide clinical recommendations on nonpharmacologic and pharmacologic management of acute pain from non–low back, musculoskeletal injuries in adults in the outpatient setting based on a systematic evidence review on the comparative efficacy and safety. The guidance is based on current best available evidence about benefits and harms, taken in the context of costs and patient values and preferences.2
- Recommendation 1:ACP and AAFP recommend that clinicians treat patients with acute pain from non–low back, musculoskeletal injuries with topical nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) with or without menthol gel as first-line therapy to reduce or relieve symptoms, including pain and improve the patient's treatment satisfaction2
- Recommendation 2: ACP and AAFP suggest that clinicians treat patients with acute pain from non–low back, musculoskeletal injuries with oral NSAIDs to reduce or relieve symptoms, including pain, or with oral acetaminophen to reduce pain.2
NICE guideline recommendation for treating sprains and strains
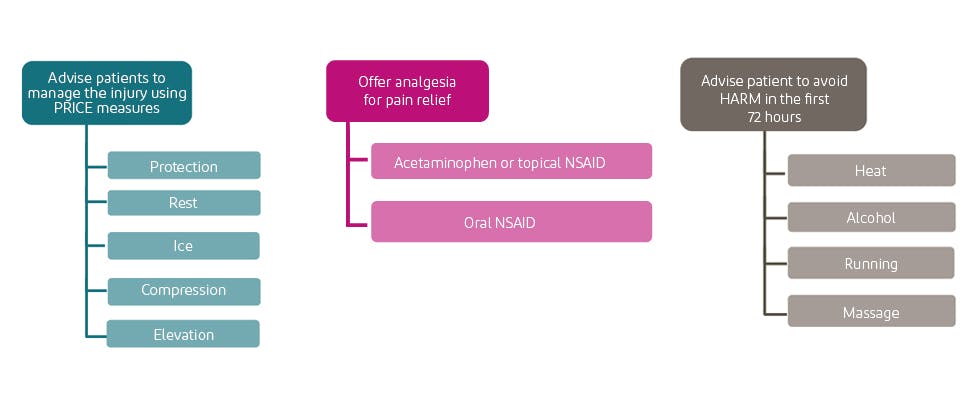
Sprains and strains can be managed simply in the first 48- 72 hours following the soft tissue injury3
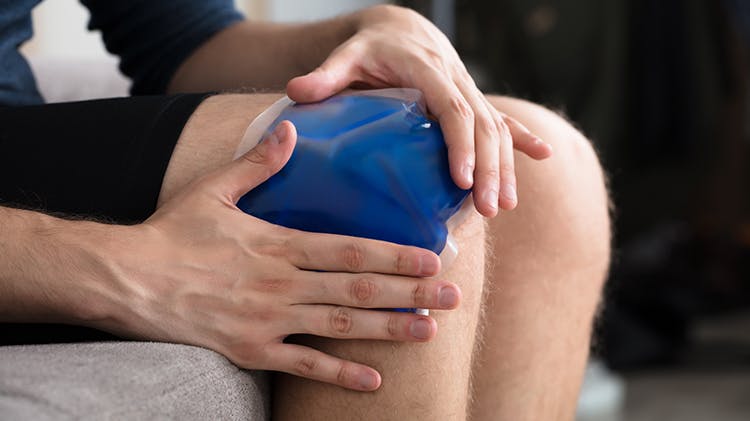
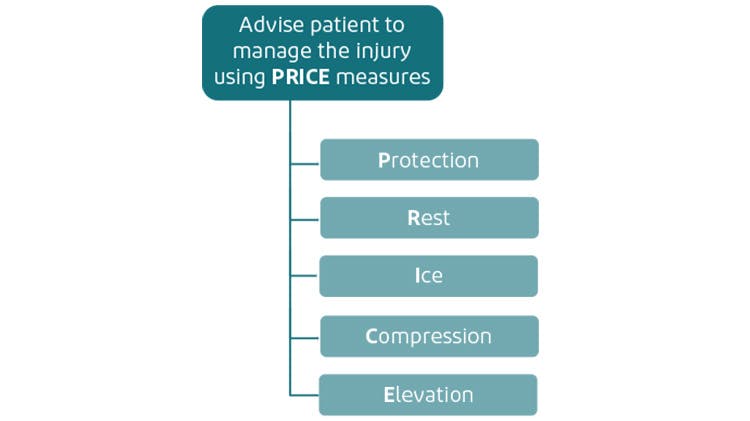
According to guidance from the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence, patients with sprains or strains should be advised to follow the PRICE protocol in the first few days after the injury.1,3,4
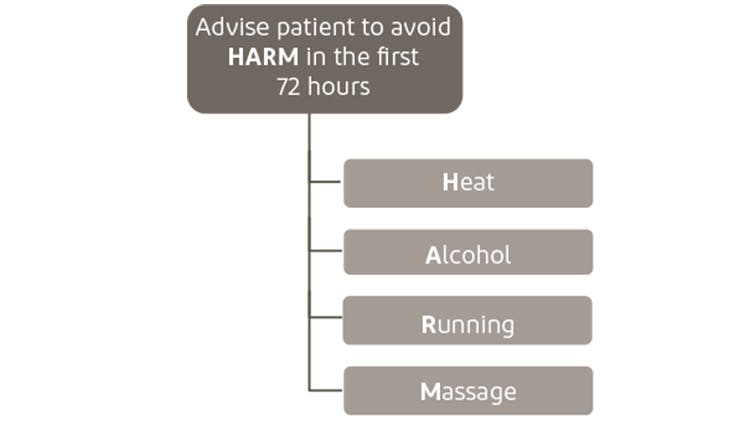
The HARM protocol identifies key factors that should be avoided for the first 72 hours post-acute injury.5
Read more about these approaches below.
Analgesics can be used to relieve pain from acute sprains and strains
Acetaminophen, topical non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) medications, or oral NSAIDs can be used to help manage acute sprains and strains.4*
* These products should not be used together.
Utilizing physical therapy to improve outcomes
After the first 72 hours, physiotherapeutic interventions can be beneficial for soft tissue injuries
Treatment and rehabilitation plans must be individually tailored to maintain and improve range of motion, reduce pain and inflammation, and improve functional activities.8
For example, massage therapy can reduce muscle soreness — although this should not be used in the first 72 hours after the injury.5
Appropriate strengthening programs using tailored exercises are often required in the longer term to maximize recovery, and training regimens may need to be adjusted.8
How can Terry & Nicola be helped?
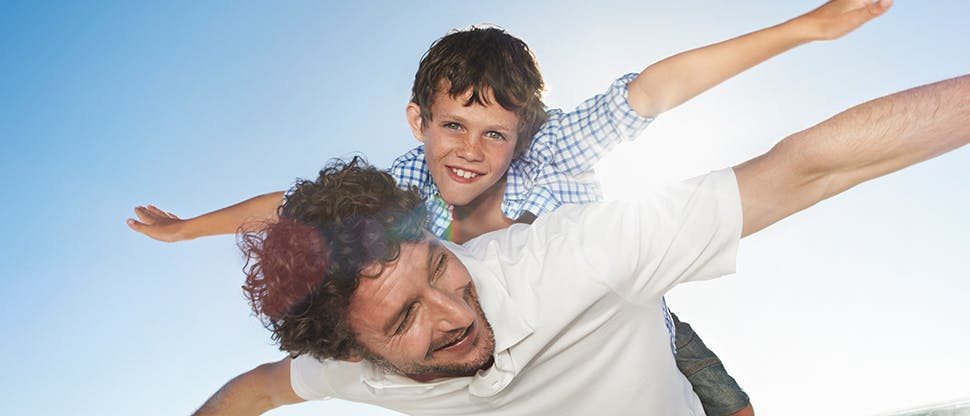

Terry
Terry* has sprained his ankle from playing tennis and is struggling to work and take care of his children.
Terry wants effective pain relief.
Voltaren is absorbed through the skin to reach the area of inflammation, providing relief from pain and inflammation after soft tissue injuries, so Terry can get back to doing the activities he enjoys.9
* Fictional case study.
![[Woman gardening]](https://i-cf65.ch-static.com/content/dam/cf-consumer-healthcare/health-professionals/en_CA/pain-relief/conditions/Nicola%20970x416.png?auto=format)
Nicola
Nicola* has strained her back after a weekend gardening and is having trouble performing everyday activities.
Nicola wants pain relief.
Advil Liqui-Gels act fast to relieve acute pain from backache so that Nicola can get back to her busy lifestyle and gardening on the weekends.10,11
* Fictional case study.
Understanding acute sprains and strains
Signs and symptoms
Explore how to recognize acute sprains and strains and learn when a referral to a doctor is necessary.
Overview of acute back and neck pain
Learn more about acute back and neck pain and meet two patients experiencing these types of acute pain.
Learn more
Voltaren products
Help your patients manage their acute, localized muscle, joint and back pain with our pain-relieving topical products.6,7

Advil — for all your patients’ acute pain relief needs
With proven efficacy in acute pain and a well-established safety profile — you can trust the pain relief of ibuprofen in Advil10

Acute Back and Neck Pain
Learn more about acute back and neck pain and how it can be relieved.