Tension-type headache and migraine causes

What are they?
Tension-type headache
Tension-type headache (TTH) is a head pain that occurs in frequent or infrequent shorter episodes (episodic*) or that is regularly or constantly present (chronic†).1 TTH are usually mild or moderate in intensity and may present as a “pressing” or “tightening” quality. It is usually not aggravated by physical activity.
Migraines
Migraines on the other hand, are severe and disabling attacks that reoccur over time and often felt on one side of the head. It has a “pulsating” quality and is often associated with changes in light, sound and odor sensitivity. It is usually accompanied by nausea and neck stiffness. Patients will experience seeing spots or stars during attacks and, feeling fatigued or dizzy after.2,3
Pathophysiology, causes and triggers of tension-type headaches
Pathophysiology of tension-type headaches4
Unlike migraines, the mechanism of TTH is not clearly known. It may originate from tensed muscles especially around the neck area and can be stress-related.
Pathophysiology, causes and triggers of migraines
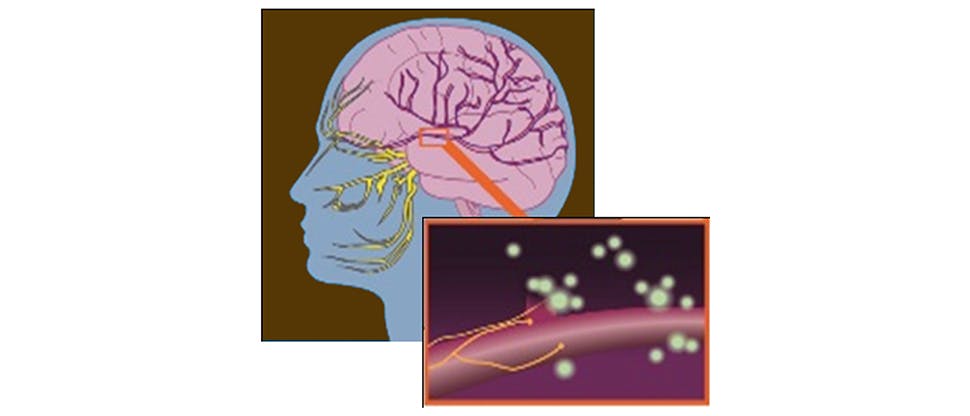
Pathophysiology of migraines6
Migraines are caused when the nerves and blood vessels around the trigeminal nerve (trigeminovascular system) located in the head are triggered to fire abnormally. When this happens, the trigeminal nerves produce and release substances called vasoactive neuropeptides, prostaglandins and inflammatory cytokines.
On release, these substances cause inflammation of the surrounding blood vessels, which in turn activates the pain receptors nearby (nociceptors). When nociceptors are activated, these sensory nerves send signals to parts of the brain responsible for producing sensation of pain such as the thalamus and cerebral cortex.
Understanding headaches
Headaches & migraine overview
Find out more about how headaches and migraines impact people’s life.
How do they present?
Find out the signs and symptoms of tension-type headache and migraine. Learn to differentiate them and learn about “red flag” symptoms that indicate a referral to a doctor.
What can you recommend to your patients for pain relief from their headaches?
Find out more about both non-pharmacological and pharmacological treatments for tension-type headache and migraine.
Learn more

Panadol Extra
With a dual formulation that fights tough pain such as headaches, migraines, dental pain and menstrual pain.
Combination of paracetamol and caffeine for tension-type headache
Discover how paracetamol and caffeine work together to help treat pains like tension-type headaches.
