Tension-type headache and migraine causes

What are they?
Tension-type headache
Tension-type headache (TTH) is the most common type of headache, and is a head pain that occurs in frequent or infrequent shorter episodes (episodic)*, or occurs regularly or is constantly present (chronic)†2. TTH are usually mild or moderate in intensity and may present with a “pressing” or “tightening” quality. It is usually not aggravated by physical activity (e.g., climbing stairs).2
Migraines
Migraines can be severe and disabling and can reoccur over time and are often felt on one side of the head.3 It has a “pulsating” quality and is often associated with symptoms of light, sound, and odor sensitivity. 3 A migraine is usually accompanied by nausea and neck stiffness, and during an attack patients will experience visual disturbances such as seeing spots or stars, and then feel fatigued or dizzy afterwards.3,4
* Less than 15 days per month. † Greater than 15 days per month.
Pathophysiology, causes, and triggers of tension-type headaches
Pathophysiology of tension-type headaches
Unlike migraines, the mechanism of TTH is not well understood.
The pathogenesis of TTH is probably multifactorial, but the precise mechanisms are uncertain.5,6 Given the wide variation in frequency and intensity in TTH, not only between individuals but within individuals over time, it is likely that the underlying pain mechanisms in TTH are dynamic and vary from one individual to another, and potentially from one attack to another in the same individual.5,6
TTH = tension-type headache.
Pathophysiology, causes and triggers of migraines
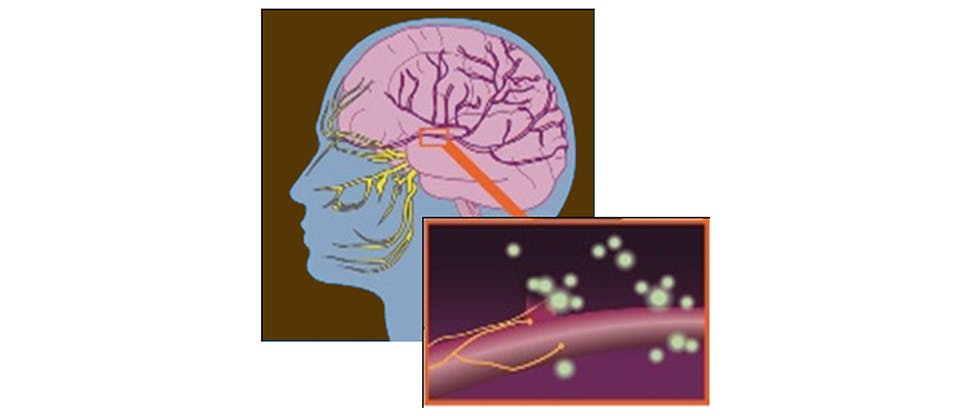
Pathophysiology of migraines
Migraines are caused when the nerves and blood vessels around the trigeminal nerve (trigeminovascular system) located in the head are triggered to fire abnormally.8 When this happens, the trigeminal nerves produce, and release substances called vasoactive neuropeptides, such as substance P, neurokinin A, CGRP, and nitric oxide.8,9
On release, these substances cause inflammation of the surrounding blood vessels, which in turn activates the pain receptors nearby (nociceptors). 8,9 When nociceptors are activated, these sensory nerves send signals to parts of the brain responsible for producing sensation of pain such as the thalamus and cerebral cortex. 8,9
CGRP = calcitonin gene-related peptide.
Understanding headaches and migraine
Headaches & migraine overview
Find out more about how headaches and migraines can impact people’s lives.
How do they present?
Find out the signs and symptoms of tension-type headache and migraines. Discover how to differentiate them and learn about “red flag” symptoms that indicate when a referral to a doctor is necessary.
What can you recommend to your patients for pain relief from their headaches?
Find out more about the pharmacological and non-pharmacological treatments for tension-type headache and migraines.
Learn more
Advil Liqui-Gels
An over-the-counter analgesic containing 200 mg ibuprofen that helps your patients manage their headache pain, including tension headache.12

Advil — for all your patients’ acute pain relief needs
Learn more about the Advil product family range.
